Recently, the Biomass and Environment Research Group of the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Guangxi University made important progress in the field of single-atom catalysis for organic pollutant degradation. The study, entitled “Coordination Reconstruction Enhanced Synergistic Nonradical Oxidation Pathways in Cobalt Single-Atom Catalysts for Sustained Pollutant Destruction,” was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The first author is Liu Lin, a Ph.D. student enrolled in 2024, while Prof. Li Zhili and Assistant Prof. Chen Bo are the corresponding authors (co-first corresponding authors). Guangxi University is the sole corresponding affiliation.

Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have attracted extensive attention in environmental remediation due to their excellent catalytic performance. However, their practical application is constrained by low synthesis efficiency, challenges in large-scale production, and high costs. To address these issues, the research team developed a scalable and cost-effective solid-state pyrolysis strategy, successfully preparing cobalt single-atom catalysts (Co-SACs) at a cost of approximately USD 35 per kilogram. By employing hydrothermal oxygen substitution to regulate the coordination environment of the single atoms, the catalysts achieved highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS). The study further elucidated the crucial role of coordination structure engineering in nonradical oxidation processes (including singlet oxygen, high-valent metal-oxo species, and electron transfer). These findings provide both theoretical insights and technical support for the controllable synthesis of SACs and the efficient treatment of high-concentration antibiotic wastewater, demonstrating significant scientific value and engineering application potential.
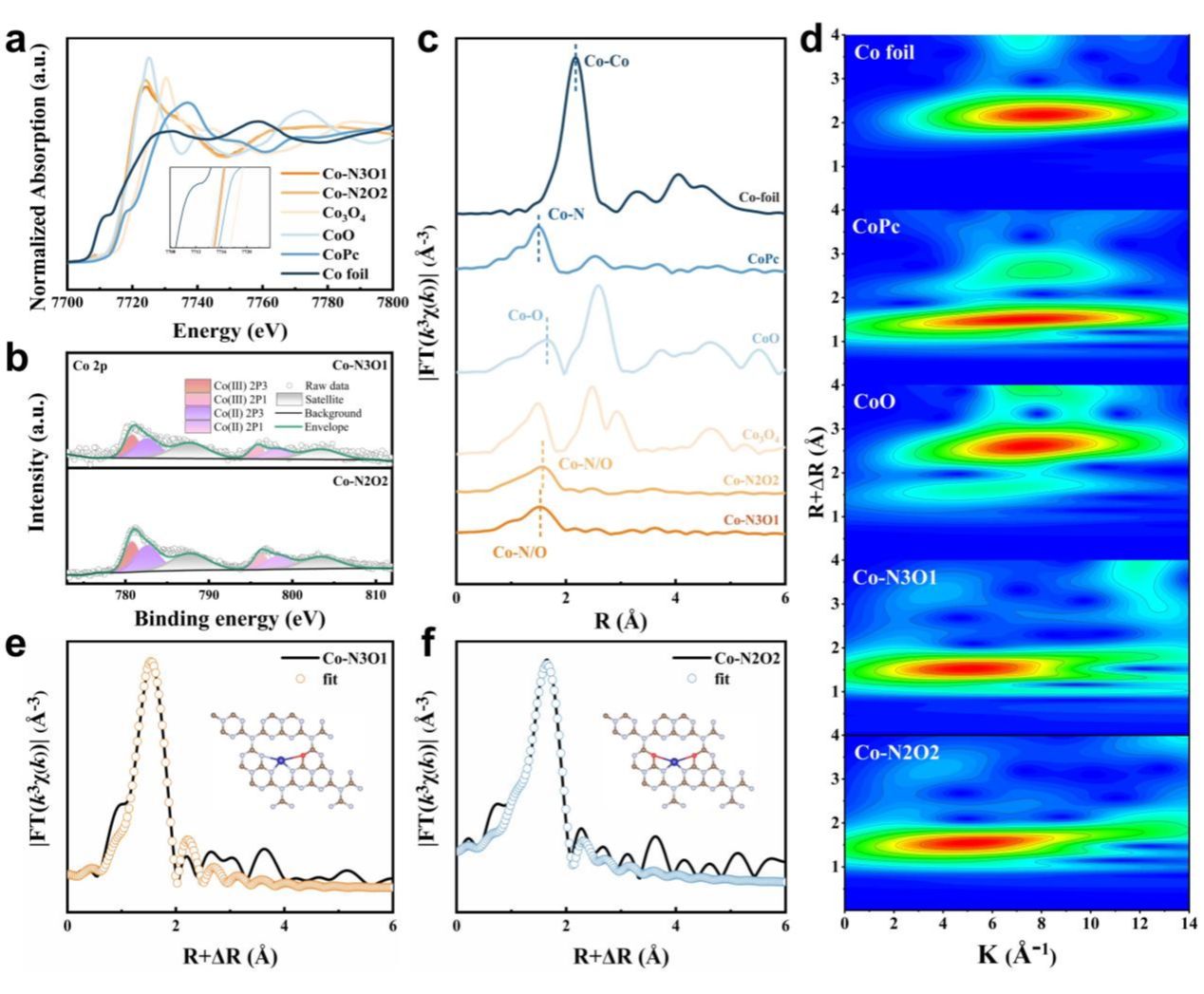
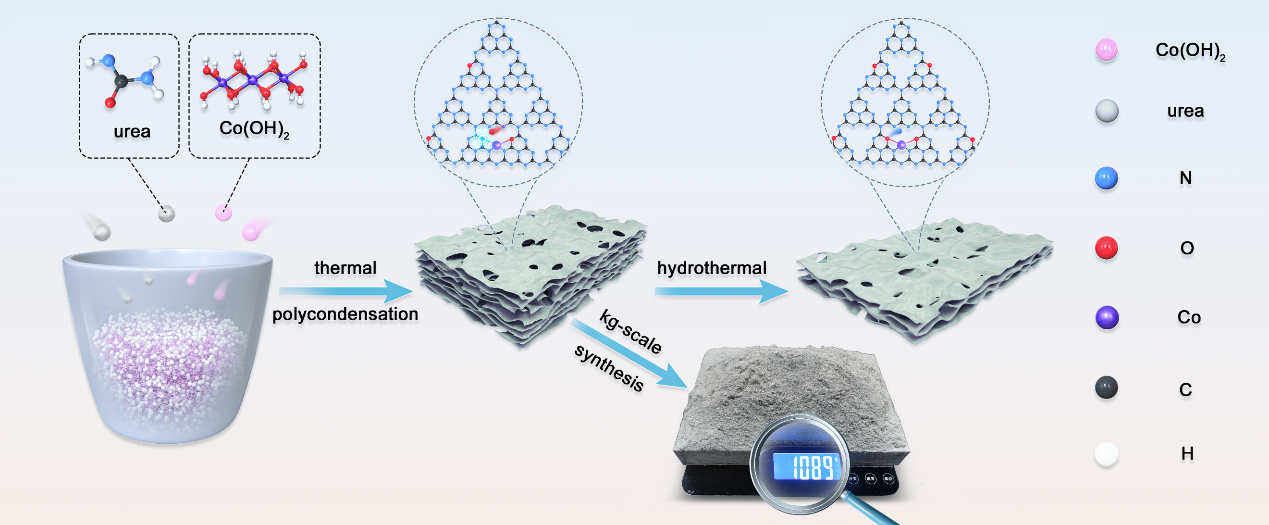
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi, and the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Resource Processing and Process Intensification Technology. In recent years, the Biomass and Environment Research Group has carried out extensive research on biomass materials development, biomass valorization, and environmental catalysis, achieving a series of high-quality results published in internationally renowned journals such as Chemical Engineering Journal, Journal of Hazardous Materials, and Journal of Materials Chemistry A. The group has also been awarded the Second Prize of the Guangxi Natural Science Award.